Crucial Raw Material
Methanol, an organic compound classified under the alcohol family, stands as one of the most abundantly produced organic chemicals. As of 2015, global methanol demand soared to 75 million metric tons, with a worldwide production capacity reaching approximately 110 million metric tons (source: www.methanol.org/the-methanol-industry).
Within the chemical industry, methanol primarily acts as a fundamental ingredient in the manufacturing of various products such as formaldehyde, olefins, acetic acid, MTBE, DME, and biodiesel. Therefore, renewable methanol emerges as an essential component in rendering a diverse range of chemical products environmentally sustainable, including polymer fibers for textiles, plastics for packaging, adhesives, solvents, and much more. In addition to its applications in the chemical, construction, and plastics sectors, methanol also serves as a fuel or fuel additive. Traditional production methods involve catalytic processes utilizing fossil fuels like natural gas or coal. However, with increasing demand, there’s a growing interest in adopting environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional technologies.
Applications of Renewable Methanol
Renewable methanol not only upholds environmental integrity but also boasts diverse applications, serving as an energy carrier for storing electricity generated from renewable sources or as a transportation fuel. Methanol can be blended with conventional liquid fuels or utilized to power systems entirely dependent on methanol. For instance, a methanol-reforming technology generates hydrogen essential for the distinctive HDW Fuel Cell System, which powers non-nuclear submarines. Prominent shipping companies are also exploring methanol’s potential as a fuel for traditional combustion engines and methanol-powered fuel cells. A significant advantage of methanol lies in its compatibility with existing liquid fuel infrastructure, which can be directly utilized or easily and inexpensively modified.
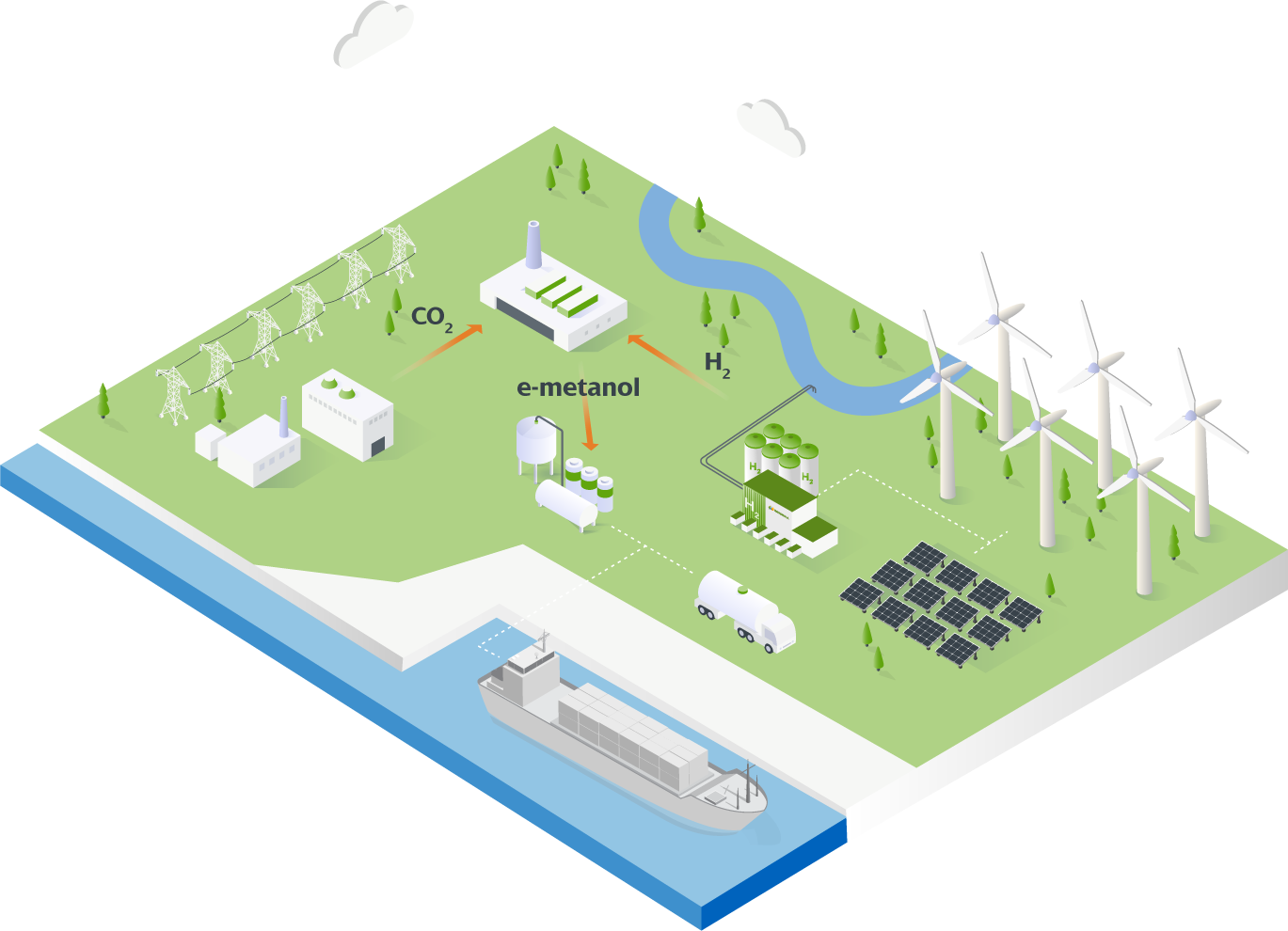
Renewable Methanol Production
For large-scale industrial plants, RBE employs its proprietary Methanol technology. Hydrogen production is facilitated by the highly efficient alkaline water electrolysis (AWE) process, based on RBE’s established chlor-alkali electrode technology. Carbon dioxide is sourced from biogas or other fermentation plants, flue gas, or waste gas. By capturing or preventing this greenhouse gas emission, the process contributes significantly to climate protection.
The electricity required for green methanol production is sourced from renewable sources such as wind power, geothermal energy, or hydropower. Consequently, this green methanol technology presents a viable option in regions abundant with renewable energy resources, supported by a legal framework promoting renewable energy and its conversion into chemicals.
Ecological and Economic Advantages
– Sustainable, climate-friendly technology.
– Customized, cost-effective solutions tailored to each operator’s needs.
– Comprehensive one-stop solutions covering EPC, plant operation, staff training, service, and spare parts, all from a single source.
Global warming is a fact
Renewable methanol as alternative fuel and feedstock for the chemical industry & manufacturing processes reduces greenhouse gas emissions.